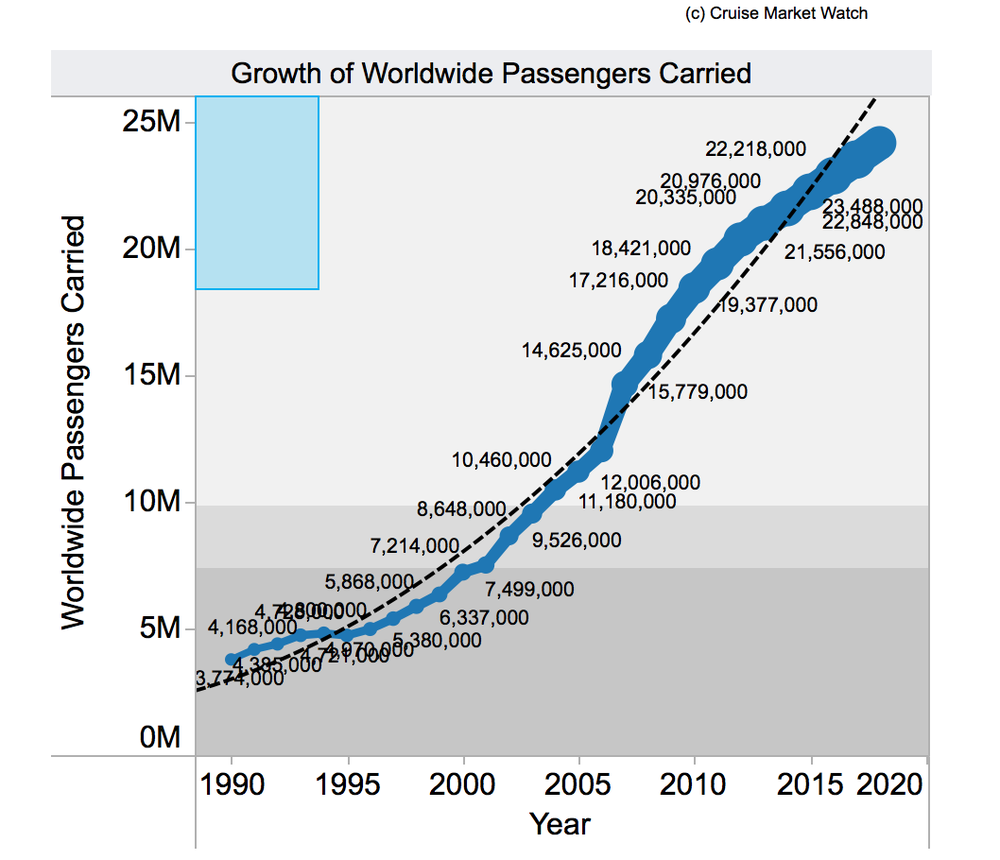
It could be time for you to put to sea as the cruise ship industry continues to grow. From 2015 to 2016, 17 more new cruise ships will come online, with more to follow.
Many of these are gigantic vessels capable of carrying thousands of passengers plus crew, dwarfing existing craft.
It is probable that vessels will grow in size until they are better compared to small cities or at-sea resort towns that do not put into port but will be tended by smaller ships and aircraft landing on the top deck.
The cost of the structural, motive, and infrastructure systems of these vessels is enormous, and require innovative construction techniques such as this covered dry dock.
The investment in facades, furnishings, lighting, decor, equipment, elevators, and other "building products" will be similarly titanic. Many are replete with shopping, theaters, dining, fitness facilities, and accommodations that would make a Las Vegas hotel seem modest in comparison.
More, older ships will be refurbished to compete.
While there will always be cramped interior cabins and crew quarters, there is also a focus is on elegant suites for those with the resources.
One reason for this tread is that rising sea levels make investment in coastal resorts a risky proposition. This accounts for the interest in floating platforms that are not necessarily designed for cruising. As population distributions shift in response to global warming, the platform can be towed to more attractive locations.
Beyond the recreational market, plans -- both serious and theoretical -- are underway for floating cities. Part of the appeal is the perception that these private islands are havens from social unrest, regulations, ecological apocalypse, and taxation.
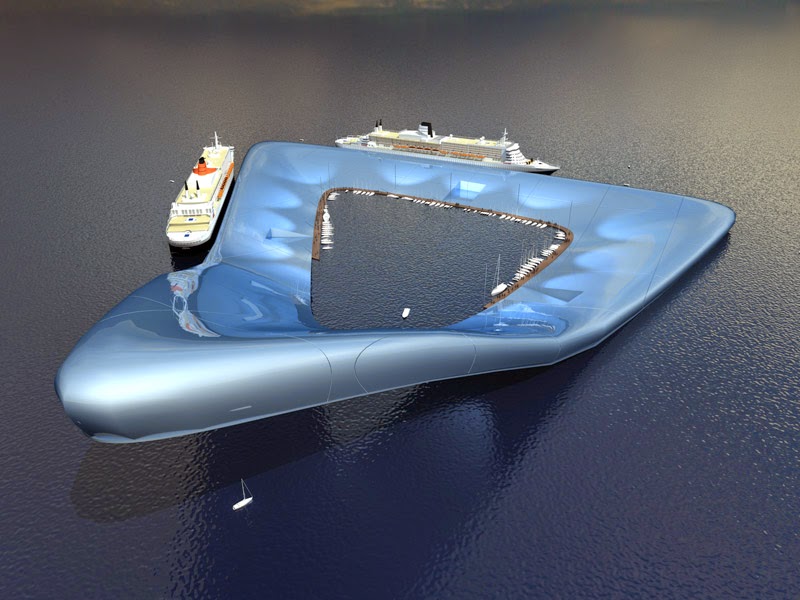
At the (somewhat) smaller end of the spectrum, many personal yachts are now being supersized, as this recent design by Zaha Hadid suggests.
Her's is not the only A/E/C firms have entered the market. They also are active in the development of ports and landside facilities in emerging markets and to accommodate larger ships.
Some terminals will become destinations in their own right with profound implications for the future of travel, conventions, business meetings, and more.
SO NOW WHAT?
Contrary to the maxim, a rising tide does not float all ships, only the businesses that are prepared.
This is a competitive global market. Many existing architectural products will require modification (or at least additional testing) to prove seaworthy. The decision making process, buyer behavior, contractual and legal implications, and many other business factors are different than land based construction.
Call me to discuss your strategy launching into this growth market.
Michael Chusid
+1 818 219 4937
michael@chusid.com
Many of these are gigantic vessels capable of carrying thousands of passengers plus crew, dwarfing existing craft.
It is probable that vessels will grow in size until they are better compared to small cities or at-sea resort towns that do not put into port but will be tended by smaller ships and aircraft landing on the top deck.
The cost of the structural, motive, and infrastructure systems of these vessels is enormous, and require innovative construction techniques such as this covered dry dock.
The investment in facades, furnishings, lighting, decor, equipment, elevators, and other "building products" will be similarly titanic. Many are replete with shopping, theaters, dining, fitness facilities, and accommodations that would make a Las Vegas hotel seem modest in comparison.
More, older ships will be refurbished to compete.
While there will always be cramped interior cabins and crew quarters, there is also a focus is on elegant suites for those with the resources.
One reason for this tread is that rising sea levels make investment in coastal resorts a risky proposition. This accounts for the interest in floating platforms that are not necessarily designed for cruising. As population distributions shift in response to global warming, the platform can be towed to more attractive locations.
Beyond the recreational market, plans -- both serious and theoretical -- are underway for floating cities. Part of the appeal is the perception that these private islands are havens from social unrest, regulations, ecological apocalypse, and taxation.
At the (somewhat) smaller end of the spectrum, many personal yachts are now being supersized, as this recent design by Zaha Hadid suggests.
Her's is not the only A/E/C firms have entered the market. They also are active in the development of ports and landside facilities in emerging markets and to accommodate larger ships.
Some terminals will become destinations in their own right with profound implications for the future of travel, conventions, business meetings, and more.
SO NOW WHAT?
Contrary to the maxim, a rising tide does not float all ships, only the businesses that are prepared.
This is a competitive global market. Many existing architectural products will require modification (or at least additional testing) to prove seaworthy. The decision making process, buyer behavior, contractual and legal implications, and many other business factors are different than land based construction.
Call me to discuss your strategy launching into this growth market.
Michael Chusid
+1 818 219 4937
michael@chusid.com